Unit 3 – ICT Skills Class 9 Notes
ICT stands for Information and communication Technology. It refers to all devices; it may be hardware components, applications (softwares) and more other systems that allow people and organizations to interact in the digital world. ICT comprises all communication technologies such as Internet, mobile phones, satellite communication, wireless/wired network etc.
UNESCO – United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization
UNESCO has defined ICT as forms of technology that are used to transmit, process, store, create, display or exchange information by electronic means.
Role and Importance of ICT
It provides the service to transmit the data with the help of different tools.
- ICT in workplace
- ICT in education
- ICT in healthcare
- ICT in Governance
- ICT in business
- ICT in daily life
- ICT in finance and banking
- ICT in entertainment
- ICT used in other fields such as architecture, arts, career, home, law enforcement, transportation and travel to perform and manage their routine based tasks.
ICT TOOLS – Mobile phone, Tablets, TV & Radio, E-mail etc.
Basic components or organization of a computer
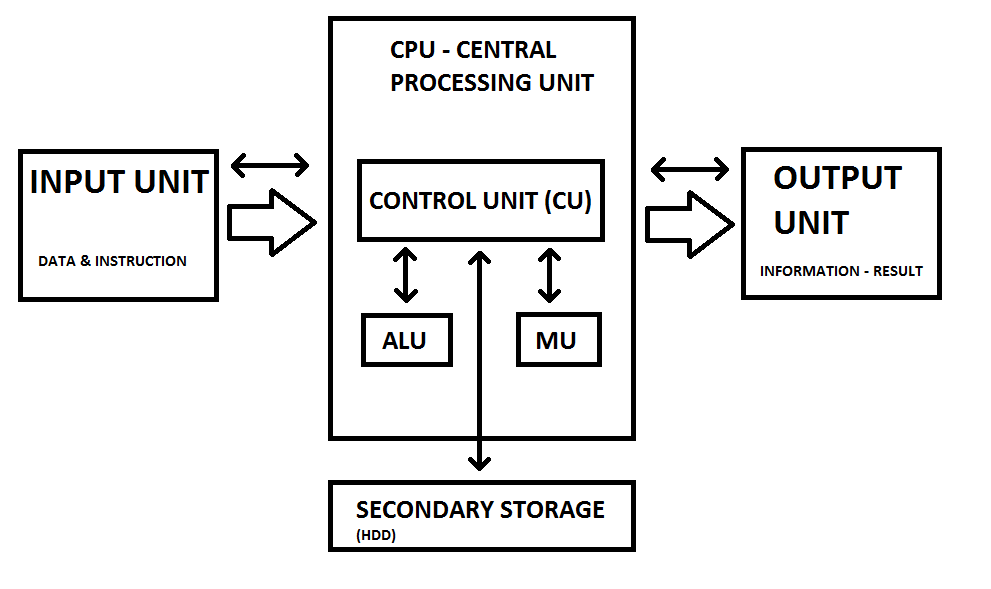
There are three main components of CPU
- ALU (Arithmetic Logical Unit) – It is a component of CPU that performs the arithmetic and logical operations like – addition, subtraction, division and multiplication. The logical operations use the relational operators like – greater than (>), smaller than (<), greater than equal to (>=),less than equal to(<=), not equal (!=) etc.
- MU (Memory Unit) – This unit controls all the operations related with all the components of a computer system. It also controls the transfer of data and instructions among the various units of a computer.
- CU (Control Unit) – It is used to store the data as well as instructions. The data and instructions can be accessed any time from the memory as it stores data permanently.
Characteristics of a Computer System
- Accuracy –
- Speed –
- Versatility –
- Reliability –
- Diligence –
- Vast Storage Memory –
Limitations of a Computer System
- Inability to take a decision –
- Inability to express ideas –
- Inability to learn and implement –
Areas of Applications of Computers
- Education and Research –
- Healthcare and Medicine –
- Business –
- Banking and Finance –
- Military –
- Scientific Research –
- Engineering –
- Manufacturing –
- Entertainment –
- Publishing and Printing Media –
- Animations and Films –
Hardware / Software (IPO / Peripheral Devices / Storage Devices / Ports / Networking Devices)
Peripheral Devices: Computer system is the combination of hardware and software that is made up of different types of units such as input, output and storage. These all connected devices are termed as peripheral devices. Example: Optical disc drive, Modem, Keyboard, Mouse etc.
Input Devices
Scanner: It is an input device that is used to scan or read different elements like text, images or other objects optically. The scanned data is then converted into a digital image and displayed on the computer screen.
There are basically three types of scanner.
1. Drum Scanner – It uses a rotating glass drum. Drum scanners are mainly used in the publishing industry to print high quality images.
2. Flatbed Scanner – These are small scanners with a flip-flop cover protecting the glass window. Flatbed scanners are mainly used in schools, homes, offices etc.
3. Handheld Scanner – Portable and manually operated device which is dragged over the surface of the image to be scanned.
Output Devices
Printer: Printers are output devices used to prepare permanent output or result on paper. Printed paper is known as “Hard Copy”.
It is a device that generates text and graphics on a physical medium like paper or sheet.
Printers can be grouped into two categories. They are as follows:
1. Impact Printer – It’s a type of printer that works with paper via direct contact with the ink ribbon (printer head). Usually, these printers are noisy but remain in use today as they are remarkable for their multi-part features.
An impact printer has the same mechanisms as the typewriter.
Example: Dot-matrix printers, Daisy-wheel printers
2. Non-impact Printers – It is a type of printer that doesn’t touch a ribbon to print it. They used technologies such as laser, electrostatic, chemical and inkjet.
In general non-impact printers are much quieter. Maintenance or repair is less likely than earlier impact printers.
Examples: Inkjet printers, Laser printers
Important points: A printer’s speed is normally shown in pages per minute (ppm). The printer’s resolution is expressed as dots per inch (dpi).
Important Full Forms
- BCR – BAR CODE READER
- CRT – CATHODE RAY TUBE
- LCD – LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY
- LED – LIGHT EMITTING DIODE
- CD-R – COMPACT DISC RECORDABLE
- CD-RW – COMPACT DISC REWRITABLE
- CD-ROM – COMPACT DISC READ ONLY MEMORY
- DVD – DIGITAL VERSATILE DISC
- BD/BRD – BLUE-RAY DISC
Memory Units (Primary / Secondary / Cache)
Units of Measuring Computer Memory
Formula : TEri Payal Eb Zhalakati YO BRO GEO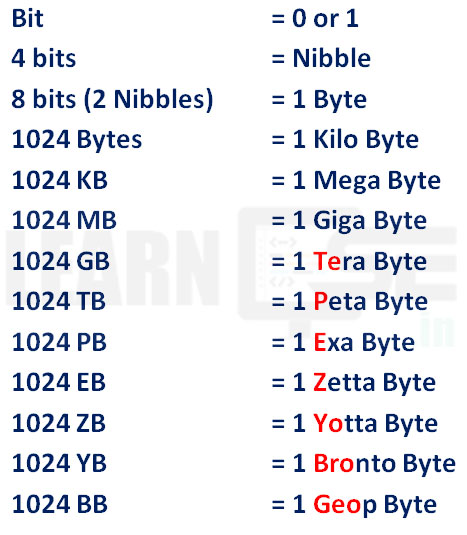
Differences between Primary Memory and Secondary Memory
| Primary Memory | Secondary Memory |
|---|---|
| 1. Primary memory is temporary. | 1. Secondary memory is permanent. |
| 2. It is directly accessible by processor or CPU. | 2. It is not directly accessible by processor or CPU. |
| 3. It is volatile in nature. | 3. It is non-volatile in nature. |
| 4. Primary memory devices are more expensive than secondary storage devices. | 4. Secondary storage devices are less expensive than primary memory devices. |
| 5. It is also known as internal or main Memory. | 5. It is also known as external or auxiliary memory. |
| 6. Example: RAM, ROM, Cache etc. | 6. Example: Hard-disk drive, Pen-drive etc. |
Differences between RAM (Random Access Memory) and ROM (Read Only Memory)
| RAM (Random Access Memory) | ROM (Read Only Memory) |
|---|---|
| 1. It is known as Random Access Memory. | 1. It is known as Read Only Memory |
| 2. It is a temporary memory | 2. It is a permanent memory that keeps information of an OS |
| 3. It is a volatile memory. | 3. It is a non-volatile memory |
| 4. It is used by application programs. | 4. It is used by Operating System |
