Unit 4 – Web Applications and Security
Session 1: Working with Accessibility Options
Common Impairments that affect the computer users are:
- Visual Impairment – It refers to a condition where an individual experiences limitations in their ability to see or process visual information.
- Hearing Impairment – It denotes a condition in which a person has difficulty hearing or processing auditory information.
- Physical Impairment – It signifies a limitation in a person’s physical abilities or mobility, often due to a medical condition or disability.
- Learning Impairment – It indicates a difficulty or challenge in acquiring and processing information or skills, often affecting one’s ability to learn in typical educational settings.
Different ways to open Launching Accessibility Options
- Start button >> Control Panel >> Ease of Access >> Ease of Access Center
- Start button >> All Programs >> Accessories >> Ease of Access >> Ease of Access Center
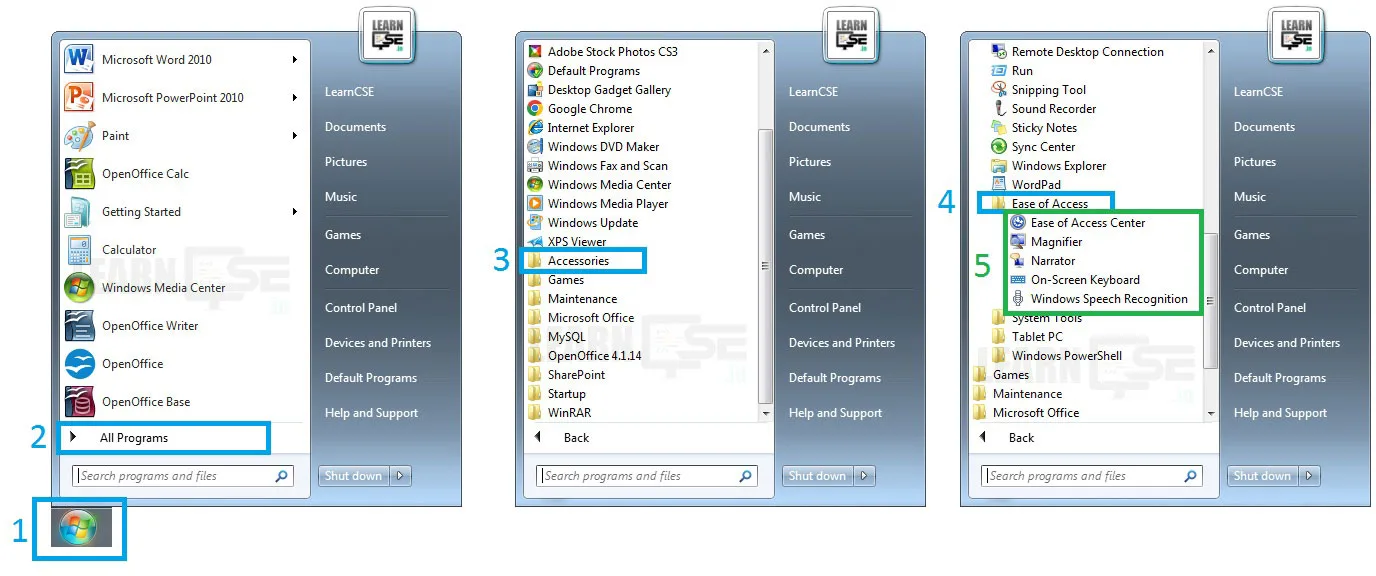
- Window Logo Key + U
- Login screen Icon
Why to use High Contrast / Color Inversion Screen?
People with weak eyesight can more easily distinguish between elements and read the text if there is a well-designed black and white theme. Usually this also comes with the option to enlarge text and elements.
Quick Access Common Tools
1. Magnifier
Steps to Open – Open Ease of Access Center Window >> Click on Start Magnifier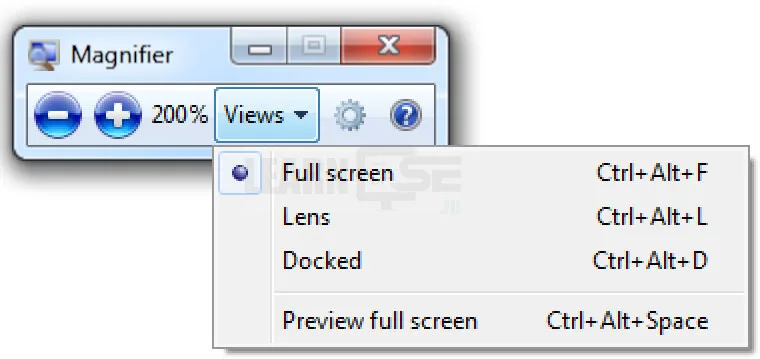
Options available in Magnifier tool
- Zoom in and Zoom out
- Views menu
- Full screen – Entire screen is magnified depending on the Zoom in (Window Key + Plus Key) and Zoom out (Window Key + Minus Key)
- Lens – Magnifies only rectangular portion of the screen
- Docked – Magnifies only a portion of the screen
2. On-screen Keyboard

Options available in On-Screen Keyboard tool
- Use click Sound
- Turn on numeric keypad
- To use the on screen keyboard
3. Start Narrator
Steps to open – Control Panel >> Ease of Access >> Ease of Access Center >> Start Narrator
Options available in Start Narrator tool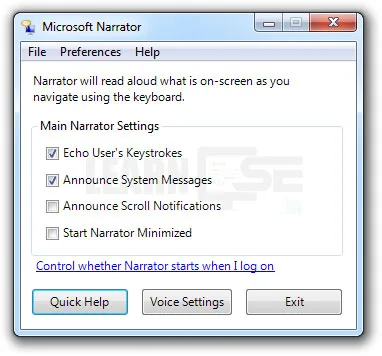
- It is a screen reader utility
- It also describes some system events, such as error messages, notifications etc.
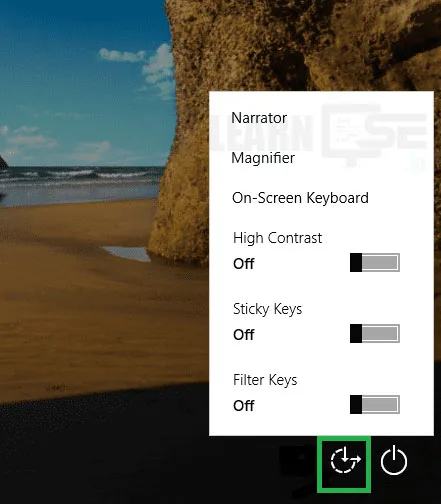
4. Set Up High Contrast
- Shortcut key to Turn On or OFF High Contrast
Left Alt + Left Shift + Print Screen (Prt Sc)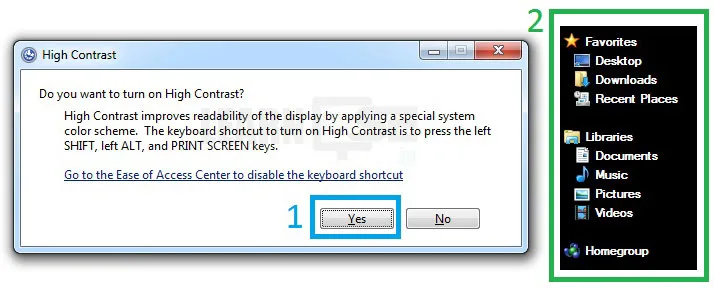
Access Mouse Keys, Sticky Keys, Toggle Keys, Filter Keys
Steps to open – Control Panel >>Ease of Access >>Ease of Access Center >>Make the mouse/keyboard easier to use
1. Sticky Keys
Sticky Keys stick your Alt, Ctrl, Del and Windows Logo button even after you release them so that you can perform windows shortcut operations without having to press both the buttons simultaneously. Suppose you have enabled Sticky keys, and you want to open Windows Explorer using shortcut keys. You can press and release Windows button and then press the E key, even after some time, to get to the Explorer window.
- Turn on/off Sticky Keys when SHIFT is pressed 5 times
2. Toggle Keys
Most of the times while typing I accidentally press the Caps Lock button instead of ‘A’ key and then continue in the uppercase realizing only after I’ve typed two to three sentences. This is where Toggle Keys feature can come in handy. After you enable this feature, you will hear a notification sound whenever you press Caps, Num and Scroll Lock keys.
- Turn on/off Toggle Keys when NUM LOCK is pressed for 5 seconds
3. Filter Keys
Filter keys are meant to ignore the repeated keystrokes you press accidentally while typing. After you enable it, don’t forget to configure the default response time, or you will have to wait forever to write a simple paragraph.
- Turn on/off Filter Keys when Right SHIFT is pressed for 8 seconds
4. Mouse Keys
Microsoft Windows accessibility feature that allows a user to control their mouse movement using the numeric pad on their keyboard. The Mouse Keys feature can be enabled and disabled through the Accessibility Options or Ease of Access Center in the Windows Control Panel.
- To activate Mouse Keys – Press Alt + Left Shift + Num Lock key combination. A tone sounds and the Mouse Keys dialog box appears. By default, the cursor will be on the Yes button.
Session 2: Networking Fundamentals
A network is a collection of two or more things connected to one another to allow the sharing of data, thoughts and ideas.
Example: Telephone network, Railway Track Network, Road Network
Computer Network
A computer network may be defined as a group of two or more computer systems or peripheral devices, that are connected together to exchange information and share resources among a wide range of users.
Types of networks
Depending on their size, capabilities, and the geographical distance the cover, a computer network can be classified as follows:
- Personal Area Network (PAN) or HAN (Home Area Network)
- Local Area Network (LAN) or CAN (Campus Area Network)
- Metropolitan Area Network (MAN)
- Wide Area Network (WAN)
Personal Area Network (PAN)
This type of network connection covers a very small area such as a home or an office cabin. Besides the computers, laptops, tablets, smart phones, printers or wireless headphones also make up the nodes of this type of network. This type of network uses Bluetooth, USB connections or the increasingly popular Wi-Fi technology. This network generally covers the range of less than 10 meters.
Local Area Network (LAN)
LAN is used in an office building or an educational campus. Ethernet cables and Wi-Fi are used to set up this type of network. Its range is up to 10 Km. Number of systems connected in LAN may vary from 2 to 1000.
LAN provides a useful way of sharing the resources between end users. The resources such as printers, file servers, scanners and Internet are easily sharable among computers.
Metropolitan Area Network
This type of network is geographically larger than LAN and covers a city. They are used by large organisations, having several branches over a city or by local government bodies like the Municipal Corporation, or the police. This type of network uses microwave transmissions or fiber optic cables to link up the network.
Wide Area Network
This is the largest type of network. It spans across several cities, countries or even the whole world. Since they use huge speed technology, so WANs are expensive network. WANs are used by multinational organistions, airlines, government agencies etc. They use routers to link up to the network. Devices used for transmission are fiber optic cables, microwaves and satellites.
- It is a Network of Networks.
- World’s largest network is – Internet
Important points to remember about MAC (Media Access Control) address
- Each node in a computer network has a unique hardware address (MAC address), which enables it to communicate effectively within the network. A Media Access Control (MAC) address is assigned by the manufacturer of the NIC (Network Interface Card). Using the NIC, a computer connects itself to a network.
- A Hardware Address is a 12-digit number, consisting of numbers 0-9 and letters A-F. It is unique (like a serial number) to each network interface. Depending on the device or operating system, it can also be referred to as a MAC address, Physical Address or Ethernet ID.
Advantages of Computer Networks
- Sharing of hardware/Software/Files
- Backup
- Cost Effective
- Minor effect of breakdowns
- Save paper and Time
Disadvantages of Computer Networks
- Initial/Setup Cost
- Administrations required
- Major effect of breakdowns
- Viruses
- Security
Network Architecture
It is an overall design of a computer network hardware and their working.
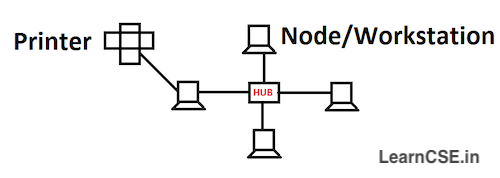
Peer-to-peer Network
Peer means equal and therefore in a peer-to-peer network, each computer or node is equal to other computers or nodes in terms of the resources that can access and share. All nodes in this type of network act both as the supplier as well as the consumer of resources. It treats all devices as having equivalent capability as shown in figure
Client-Server Network
In client-server network, there is a powerful central node (host) which has more resources than the other computers (clients) connected to the network. The central computer is known as Server and the rest computers termed as clients/nodes or workstations. The server is responsible for providing all the information and resources to the clients as per their request.
The client sends request to the server for services. The client utilizes resources of the server but does not share its resources with any other client computer.
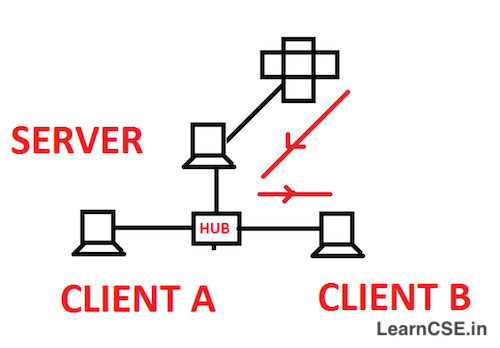
Difference between Peer-to-Peer and Client-Server Networks
| Peer-to-Peer Networks | Client-Server Networks | |
| 1 | All computers can access resources equally. All computers work equally | A server computer, more powerful than the others |
| 2 | Each computer can request for services and also provide to other computers | Client can request for services and cannot share with others |
| 3 | Each computer can store its own data | Data stored in centralized computer i.e. Server |
| 4 | It is less expensive as compare to Client-Server network | It is more expensive as compare to P2P networks |
| 5 | Easy to emplement | Not easy to implement |
| 6 | No effect on speed | If all computers request for services simultaneously, it will reslut in slowing down the server |
| 7 | Security is major concern with this type of networks | Security is less concern with this type of network |
| 8 | Is is usually implemented for a smaller number of computers in a limited area. Example: phone to phone | It is usually implemented for a large number of computers in a large area. Example: Office building, Educational campus |
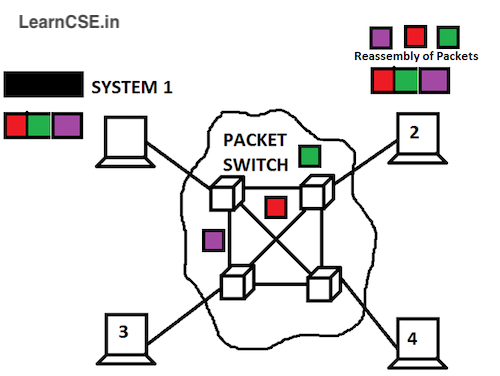
Packet Switching
Packet switching is a method of transferring the data to a network in form of packets. Packets are made of a header and a payload. Header and payload holds information of packets. In packet switching the message is broken into series of packets. Each of these packets has a header which contains information about the destination as well as reassembly instructions. The TCP/IP (transmission Control Protocol/Internet protocol) uses packet switching techniques to transfer messages or data through the Internet.
- Advantage: It is found to be more efficient for large networks.
- Disadvantage: If the packet is lost, the sender has to transmit the data again.
Network Components
Some hardware devices are required to connect the two or more computers or devices for proper functioning and data transmission. These such devices are considered as networking components.
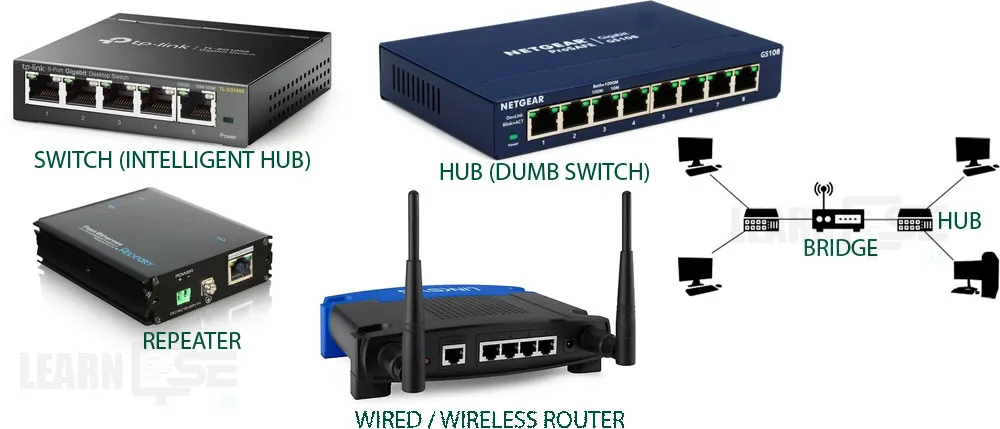

SWITCH – A network switch is a device, which connects different computers and devices on a computer network. A switch receives data, process it and then forwards it only to the destination device. It uses packet switching techniques to transfer data on the network.
HUB – A hub is a networking device which is similar to a switch. But unlike a switch which transmits the information to a particular device, a hub transmits the received information to all devices that are connected to it. Hubs are known as Dumb Switches. Hubs are comparatively cheaper than the switches.
REPEATER – A repeater simply copies the information arriving at its input and retransmit it from the output. The weakened or distorted signals at the input are regenerated and then retransmitted by the repeater.
ROUTER – A router is a networking device that is designed to forwards data packets between computer networks. A router examines a destination IP address of a given data packet, and it uses the headers and forwarding tables to decide the best way to transfer the packets. Routers perform the traffic directing functions on the Internet. Data sent through the internet, such as a web page or email, is in the form of data packets. It can be internal or external.
BRIDGE – In terms of networking, a bridge network is a Link Layer device which forwards traffic between network segments. A bridge can be a hardware device or a software device running within a host machine’s kernel.
The bridge works at the Data link layer (layer 2) of the OSI model.
The data link layer ensures that all packets of information are passed on free of errors
Types of Internet connections
- Dial-up Connection (Username / Password based)
- DSL (Digital Subscriber Line) – It transports high-bandwidth data over a simple telephone.
- Cable Internet – It runs through an underground cable network or the same cables used for cable TV. It is faster than DSL. highly reliable and isn’t prone to outages due to storms, like satellite internet.
- Satellite Connection (Broadband)
- 3G, 4G and 5G System
- Wi-Fi Wireless Fidelity (lasting support) – A data technology that allow users to access high-speed internet without the need for cables.
- Wi-Fi Hotspot
- WiMax (Worldwide Interoperability for Microwave Access)

Session 3: Introduction to Instant Messaging
Explore/read about the applications.
- Google Hangout
- Google Meet
- eBuddy
- Microsoft Team
- Skype
Session 4: Chatting with Contact – Google Talk
Session 5: Creating & Publishing Web Pages – Blog
Session 6: Using Offline Blog Editors
Define blogger
Blogger is a person who can create or update their own websites or blogs.
Names of Different Online Blogs
Online Blogs – Blogger, WordPress, Weebly, Tumblr
Names of Offline Blogs
Offline Blogs – Windows Live Writer, Qumana, BlogDesk, Thingamablog, ScribeFire
Advantages of the Offline Blogging
- It lets you concentrate better because there are no online distractions.
- Your creativity can shine without interruptions, and you can make your content top-notch with careful editing.
- You can also write in places without Wi-Fi.
- It offers privacy and helps you manage your time well when you go online to format, add images, and share your work.
What is the purpose of WYSIWYG editor?
The purpose of WYSIWYG (What You See Is What You Get) in blog editor is to get instant preview of the created Post.
Write some points to keep your Passwords Strong
- Always create a unique password for each account.
- Do not store/save password s in your web browser unless you are are the only one to use that browser.
- Use strong password as combination of small/large characters, symbols and numbers.
- Keep the length of passwords atleast more than 12 characters (according to the websites/applications)
- Do not use easy to guess passwords like mobile number, date of birth, username etc.
Example of strong password – Qw3rtyk3y80@RD
Weak password – hemantbajaj
Session 7: Online Transactions
Explain the term ‘No Compulsive Shopping’
A user buys the products at his will and as per his choice anytime and anywhere. There are no salesman around, doing hard selling and influencing the customer to buy.
Session 8: Internet Security
Purpose of Internet Security
Internet security is a central aspect of cyber security, and it includes managing cyber threats and risks associated with the Internet, web browsers, web apps, websites and networks. Internet security consists of a range of security tactics for protecting activities and transactions conducted online over the internet.
These tactics are meant to safeguard users from threats such as hacking into computer systems, email addresses, or websites; malicious software that can infect and inherently damage systems; and identity theft by hackers who steal personal data such as bank account information and credit card numbers.
The internet is mostly private and secure, but it can also be an insecure medium for exchanging or sharing information. With a high risk of intrusion by hackers and cyber criminals, internet security is a top priority for individuals and businesses alike.
Difference between Spoofing and Phishing
Spoofing tricks you as trusted source into giving up sensitive financial data or information to a cyber crook. Phishing is tricky emails, messages, calls to get sensitive information from the user.
Spoofing is means of delivery, while phishing is a method of retrieval.
Email Spoofing: The goal of email spoofing is to trick recipients into opening or responding to the message. It is a form of cyber attack in which a hacker sends an email that has been manipulated to seem as if it originated from a trusted source. Email spoofing is a popular tactic used in phishing and spam campaigns because people are more likely to open an email when they think it has been sent by a known and trusted sender.
Chat Spoofing: It is a one in which when a computer system or a user of computer false to be another identity while engaging in chat. Hiding / faking the identity of another person over the chat or internet is called chat spoofing.
Email Phishing: It is when attackers send malicious emails designed to trick people into falling for a scam. The intent is often to get users to reveal financial information, system credentials (username/password) or other sensitive data.
It is an example of social engineering that scam and manipulate the human psychology.
Phishing emails typically use generic salutation such as “Dear valued member”, “Dear account holder”, or “Dear customer”. If a company you deal with required information about your account, the email would call you by name and probably direct you to contact them via phone.
Best Practices for Internet Security
- Keep your passwords strong and safe
- Follow https instead of http to make secure transactions
- Install updated and genuine antivirus / antispyware softwares
- Keep firewall ON in a network
- Never open the attachments from unknown / unauthorised sources
- Scan all portable devices (storage/media) before use
- Restrict the number of users to use your device/computer
- Never use pirated or duplicate softwares
- Backup your all important information or data
- On the daily/monthly basis, clear cookies or cache from the device
- Never leave your computer unattended
- Make a bootable disk / start up disk of an OS
- Use encryption and decryption technique to send or receive the sensitive data
Cache
Cache, which is pronounced “cash” (not “catch” or “cashay”), stores recently used information so that it can be quickly accessed at a later time. It keeps track of things you’ve used recently so that the next time you need them, they’re right there, ready to go. This makes your computer work faster and perform better. Common types of caches include browser cache, disk cache, memory cache, and processor cache.
For example: If you’re exploring a website. Your computer’s browser takes note of all the important elements on that page, like the text, pictures, CSS or JavaScript. Now, when you move to another page on the same website that uses the same pictures or other elements, your browser doesn’t need to download everything again. It will just grab the saved data from your computer’s memory (that’s the cache) instead of fetching it from the internet.
Cookies
Cookies are small text files (size in kb) with small pieces of data — like a username and password. Specific cookies known as HTTP cookies are used to identify specific users and improve your web browsing experience. For example, they remember who you are, so you don’t have to log in every time. This makes your experience on the web smoother and more personalized.
Unit 4: Maintain Healthy, Safe and Secure Working Environment
Chapter 13. Health, Safety and Security at Workplace
Health, safety, and security are essential in every workplace to ensure the well-being of employees and prevent accidents or harm. Employers and employees must work together to create a safe environment where risks are minimized. For example, wearing helmets at a construction site or using proper lighting in an office can prevent injuries and promote safety.
Policies and Procedures for Health, Safety, and Securisty
Every workplace should have clear policies and procedures to address health, safety, and security. These guidelines help employees know how to handle emergencies and prevent risks.
- Health Policy: Offering medical check-ups or providing clean drinking water.
- Safety Policy: Ensuring fire extinguishers are available and working.
- Security Policy: Using ID cards or biometric systems to monitor access to the workplace.
Reasons for Health, Safety, and Security Programs or Policies in the Workplace
Health, safety, and security programs in the workplace are very important. They keep employees safe and help prevent injuries or health problems. For example, giving employees comfortable chairs can stop back pain. A safe workplace also helps employees work better and faster because they feel good and secure. These programs also make sure the workplace follows laws, so the company doesn’t get into trouble. Fewer accidents mean less money spent on medical bills and damages. A workplace that takes care of safety is also liked by employees and partners, which helps the company do better overall.
Workplace Safety Hazards
1. Physical Hazards
These are risks that can physically harm employees while at work.
- Working in extreme temperatures, such as very hot or cold environments, can lead to heatstroke or hypothermia.
- Repeated heavy lifting without proper techniques can cause back injuries.
- Sharp tools or machinery without safety guards can cause cuts or amputations.
2. Fire Safety
Fire is a very serious Hazard at a workplace. It can cause major financial losses to a business and also result in loss of human lives. Prevention is absolutely critical when dealing with fire safety, and there are many different rules that can be implemented to reduce the risk. Let us learn about some fire safety rules.
Fire Safety Rules
- Carry out a fire safety risk assessment
- Keep the workplace clean
- Maintain electricity safety
- Keep electrical control panel accessible
- Store chemicals safely
- Prevent ignition in explosive areas
- Conduct fire safety trainings and regular drills
- Fit relevant equipments
- Mark the exits
- Access the important information
3. Slip & Trips
Slips happen where there is very less friction or traction between the footwear and walking surface.
Trips happen when a person’s foot collides (strikes/ hits) with an object; causing one to lose the balance and eventually fall.
Some of the Common Causes of Slips and Trips at Workplaces
- Poor lighting
- Poor housekeeping
- Occasional spills
- Trailing cables
- Weather hazards
- Unsuitable floor coverings
- Loose, unanchored rugs, or mats
- Uneven or damaged floor surfaces
- Contaminated floor surfaces due to liquid or grease
- Obstructed view
- Uncovered cables
Preventions of Slips & Falls at the workplace
- Keep walking surface clean and free of clutter (covered or filled with untidy collection of things)
- Use clear and well-placed signage (for gap, uneven surface etc)
- Use Stairways / handrails
- Proper lighting
- Wear footwear
- Provide step stools / ladders
- Check floor conditions
- Manage cords / wires
- Clean up spills (liquid leakage) immediately
- Carry out regular risk assessments
4. Electrical Safety
Electrical safety at work is crucial to prevent accidents. It keeps people safe from shocks and fires, ensuring a secure environment. Following safety measures helps avoid injuries and damage, keeping everyone protected at the workplace.
Electric Safety Program should be established by all Organisations and followed properly.
- Electrical installations should be done and maintained by a competent person and checked regularly.
- Extension cables, plugs, sockets, and other flexible leads and their connections that are particularly prone to damage should be visually checked, maintained, and where necessary, replaced before using any equipment.
- Correct cable connectors or couplers should be used to join cables together; taped joints should not be allowed.
- Socket outlets should not be overloaded by the use of adaptors.
- Electrically powered equipment should be used.
- Fixed electrical equipment should have a clearly identified switch to cut off power in an emergency.
- A fuse protects the device from over current. It is designed to ‘blow’ and cut off the electricity when the current exceeds its rated capacity.
- It is important to ensure that the correct fuse is used for all appliances.
- Employees working in areas where there are potential electrical hazards must be provided with appropriate, safe, and tested protective equipment.
Potential Sources of Hazards in an Organisation
- Hazards Using Computers: Using computers for long hours can cause eye strain or wrist pain.
Solution: Use screen filters and take regular breaks. - Handling Office Equipment: Improper use of equipment like paper cutters or printers can cause injuries.
Solution: Train employees to use equipment safely. - Handling Objects: Lifting heavy objects incorrectly can lead to back injuries.
Solution: Provide training on proper lifting techniques. - Stress at Work: Work pressure can cause mental health issues.
Solution: Promote work-life balance and provide counseling. - Working Environment: Poor lighting, ventilation, or noise can impact health.
Solution: Ensure proper lighting, ventilation, and soundproofing where needed.
Chapter 14. Workplace Quality Measures
Ensuring clean air and water in the workplace is essential for employee health. Regular checks for pollutants, proper ventilation, and clean water supply prevent respiratory issues and waterborne diseases.
more content we will add soon…
Chapter 15. Prevent Accidents and Emergencies
Primary Goal of First-Aid
First aid is emergency care given immediately to an injured person. The purpose of first aid is to minimize injury and future disability. In serious cases, first aid may be necessary to keep the victim alive.
There are many situations in which the immediate first aid is necessary even before the patient is taken to a hospital. Some such situations that might occur in work places are accidents, seizures, heart attacks, shock, bleeding, poisonings, burns, temperature extremes, musculoskeletal injuries, bites and stings, medical emergencies, and employees trapped in confined spaces.
The type of First-Aid equipment and training required, in a workplace, depends on:
- The number of employees
- The types of hazards present in the workplace
- The travel distance to a hospital/availability of professional medical assistance
Compiling a risk assessment is important as it will help determine the first aid requirements. The risk can be considered low or high depending on the workplace. A low-risk workplace is one where employees are not exposed to hazards that could result in a serious injury or illness. Examples of low-risk workplaces include offices, shops, or libraries. A high-risk workplace refers to a workplace where employees are exposed to hazards that could result in a serious injury or illness and require first aid, for example factories with boilers or motor vehicle workshops.
Benefits of having a proper First Aid Training Program:
- Creates a more positive and safe working environment
- It provides quick medical response during a workplace accident
- Provides employees with transferable skills
- Satisfies legal and moral obligations
First Aid Training Course should cover the following Drills or Practices
- Burns Poisoning Shock Broken bones No pulse
- Choking Heart attack Eye injuries Heatstroke
- Respiratory (breathing related) emergencies
- Wounds (cut) causing heavy bleeding
- Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR)
Organization that Work in Field of Safety, Health and Welfare of People
OSH – Occupational Safety and Health; OHS – Occupational Health and Safety; WHS – Workplace Health and Safety (all are same)
Natural Hazards
- Atmospheric / Meteorological: Heavy rains, floods, tsunami etc. (cause by extreme weather events)
- Geological: Landslides, earthquakes etc. (caused by changes in earth surface)
- Biological: Fever (Dengue, Malaria), Influenza etc.
Explore Hazards Signs and Symbols
- General Warning
- Flammable Material
- Explosion Risk
- Toxic
- High Voltage
- Laser Radiation
- Bio Hazard
- Oxidising
- Hot Surface
- Danger of death
- Slippery Floor
- Watch your steps / Trip
- High Temperature
- Danger of Suffocation
- Electricity
- Battery Hazards
- Rotating parts
- Low temperature
- Optical Radiation
- Radiation

very well explained thanks